OIF Completes Successful 2020 Joint Network Operator, Multi-Vendor Transport SDN API Interoperability Demonstration
Public webinar, read-out events planned for Q1 2021
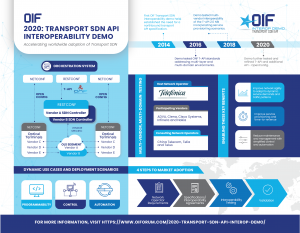
Fremont, Calif.—December 2, 2020 – OIF today announced the completion of its multi-vendor 2020 Transport SDN Application Programming Interface (API) Interoperability Demonstration. To validate the benefits of transport SDN worldwide and transport network transformation for the 5G era, OIF members participated in a ten-week long interoperability testing exercise in Telefonica’s Madrid lab.
The testing focused on SDN-based programmability, control and automation — testing Layer 1 and Layer 0 OTN control using ONF T-API 2.1.3, with additional testing of OpenConfig device APIs for transport equipment in network-operator-defined use cases.
“Operators have demanded more open optical networks to enable flexibility, lower costs, and best-of-breed options,” said Scott Wilkinson, Lead Analyst at Cignal AI. “Standard management interfaces and multi-vendor interoperability are critical to open optical networks. The interoperability demonstration recently performed under the guidance of the OIF is a major step towards achieving those operator goals.”
Participating vendors included ADVA, Ciena, Cisco Systems, Infinera and Nokia. Network operator Telefonica hosted the demo. China Telecom, Telia and TELUS participated as consulting network operators.
“The successful completion of the OIF 2020 Transport SDN API interoperability demonstration is a significant milestone toward widespread SDN deployment in production networks,” said Arturo Mayoral, Telefónica Transport Global CTIO Unit – Technology Expert and Lead of Optical SDN strategy. “By aligning vendors for a shared purpose – interoperability – and testing multiple use cases, we’re fostering manageability and flexibility in the network to allow deployment of cloud-based services, meet dynamic bandwidth demands and accelerate transport network transformation for the 5G era.”
The much-anticipated results of the multi-vendor demonstration will be revealed during a public read-out webinar event being held in partnership with Lightwave, Tuesday 12 January 2021, 6:00-7:30am PST. Register for free here.
A private read-out event for demo participants and invited Network Operators is scheduled for Tuesday 19 January 2021.
OIF representatives will give presentations on the current status of the 2020 OIF Transport SDN API Interoperability Demonstration during the below events:
NGON & DCI World Digital Symposium – Friday 04 December 2020 – 20:00-20:15pm CET, OIF Speaker: Arturo Mayoral López de Lerma, Telefonica S.A
ECOC – Monday 07 December 2020 – 17:20-17:40pm CET, OIF Speaker: Arturo Mayoral López de Lerma, Telefonica S.A
Additionally, OIF developed an infographic to visually explain the 2020 Transport SDN API Interop Demo. Print and web-ready files can be downloaded here: https://1drv.ms/u/s!AgxJQTMC3jSUiIhCVZzu9vewlRGU0w?e=hl5D3C
A technical white paper and an executive summary of the demo result will be available in Q1 2021.
Additional information can be found at https://www.oiforum.com/technical-work/2020-oif-transport-sdn-api-interoperability-demo/
2020 Transport SDN Application Programming Interface (API) Interoperability Demonstration PR Boilerplate:
Leading the acceleration of the commercialization of transport SDN worldwide and transport network transformation for the 5G era, OIF will bring new use cases and deployment scenarios into Telefonica’s lab to test multi-vendor interoperability of Layer 1 and Layer 0 OTN control using ONF T-API 2.1.3 and OpenConfig Transport APIs. The 2020 Transport SDN Application Programming Interface (API) interoperability demonstration builds on OIF’s previous transport API requirements and interoperability demonstrations which substantiated T-API as the northbound interface (NBI) of choice, establishing a foundation for open, programmable networks that allow network operators to efficiently deliver dynamic multi-domain connectivity services to the market.
About OIF
OIF is where the optical networking industry’s interoperability work gets done. Building on 20 years of effecting forward change in the industry, OIF represents the dynamic ecosystem of 100+ industry leading network operators, system vendors, component vendors and test equipment vendors collaborating to develop interoperable electrical, optical and control solutions that directly impact the industry’s ecosystem and facilitate global connectivity in the open network world. Connect with OIF at @OIForum, on LinkedIn and at http://www.oiforum.com.
PR Contact:
Leah Wilkinson
Wilkinson + Associates for OIF
Email: leah@wilkinson.associates
Office: 703-907-0010

 OIF project with a scope that focused on interoperability at a specific distance, reinforces OIF’s critical role in creating solutions to fulfill industry requirements and accelerating market adoption of optical networking technologies.
OIF project with a scope that focused on interoperability at a specific distance, reinforces OIF’s critical role in creating solutions to fulfill industry requirements and accelerating market adoption of optical networking technologies.